Yagasaki Katsuma, emeritus professor of Ryukyu University, has been constantly sounding the alarm about the problem of internal exposure related to nuclear weapons testing and nuclear electricity generation. Since the explosion at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant (NPP), he has drawn on his expertise to conduct field research, and to support those who evacuated to Okinawa. We asked him to reflect on the five years since the accident at Fukushima Daiichi, and to lay out the issues that lie ahead.
Heading to the blast site 12 days post-explosion
On March 17, 2011, a friend who lived in Fukushima City contacted me. “They’re reporting an onslaught of radioactivity, but we have no idea about any of that”, he said. “We need dosimeters, but there’s no way to get our hands on them.”
I ended up making my way to Fukushima along with several dosimeters for measuring radioactivity. I set up the dosimeters. Fukushima was under a petrol provision restriction, and I could not travel freely. I needed to make arrangements for an “emergency vehicle” to use. I had left Okinawa on March 24, traveled via Osaka by plane to Fukushima Airport, and entered Fukushima City by a bus that went through Kōriyama. The Japan Railways (JR) trains had stopped running. It had been 12 days since the first explosion, which had occurred at reactor No. 1 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP). It snowed the next morning, and I saw that a torrent of radioactivity – 12 microsieverts/hour – was relentlessly falling on the living spaces of Fukushima’s citizens.
From March 25 to 31, I went to eight areas to measure radiation doses in the air, farmland and water: Fukushima City, Iwaki City, Aizu-Wakamatsu City, Kitakata City, Minami-Sōma City, Kōriyama City, Iitate Village, and Kita-Shiobara Village. I engaged in discussions with farmers and other locals about what steps they should take.
At the time, the dose readings from farmland went down by half when just the top layer of weeds and straw litter were removed; digging 3 cm deep reduced the readings by 80%. So I suggested that if people did not plant crops this year, and removed 5 cm of topsoil from their land, they could prevent future batches of crops from radioactive contamination. It was a situation in which both national and local governments were at a loss about what to do; they could not even come up with countermeasures, and were practically without policies. In the end, apart from a few enterprising farmers who followed my recommendations, most farm-owners felt compelled to plant crops, and ended up ploughing the soil to spread radiation up to 20 cm deep.
Of the 2 dosimeters I had brought with me to conduct my survey, I lent one to a farmers’ union for one year, thus doing what I could for them in terms of temporary assistance.
No Measures to Protect Residents
One of the things which stunned me was the absoluteness of the safety myth (anzen shinwa). Even though radioactive dust was falling, no one knew anything about how to protect their bodies. The local governments had not a single dosimeter among them. The evacuation manual for NPP accidents used in Fukushima City’s elementary schools was exactly the same as the evacuation manual for earthquakes.
Furthermore, all attempts to talk about demonstrations of the danger of NPPs were categorically suppressed. Herein lies the root of why no countermeasures were taken to protect residents from radioactivity. No stable iodine tablets were distributed; no SPEEDI (System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information) data was announced, and so on.
Before the accident, I had published a book called Concealed Radiation Exposure in 2009 with Shin Nihon Shuppansha, which expounded my view that internal exposure was a hidden kind of exposure more dangerous than external exposure.
The Atomic Bomb Casualty Commission (ABCC) and the Radiation Effects Research Foundation (RERF) have suppressed information about those sacrificed in the atomic bombings. The International Commission for Radiation Protection (ICRP) has concealed the issue of internal exposure in the context of their commitment to the cause of the United States’ nuclear strategy.1 The Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident, through multiple explosions, has scattered between one hundred and several thousand more radioactive materials than the Hiroshima bomb into the environment, resulting in health damage caused by internal exposure. This would ineluctably lead the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the ICRP to cover up internal exposure and exposure casualties. In other words, I believed that they would do everything they could to cast off health damage to Fukushima residents, and support the Japanese government’s policies to abandon its own citizens. This is what drove me to rush down to Fukushima.
The Accident on Televised Programmes
For two years in 2011 and 2012, I delivered more than 120 lectures each year, and held interviews with the mass media. The mass media did courageously report on the reality and danger of internal exposure, but a distressing incident occurred in the process. This happened during my appearance, on July 2, 2011, as a guest on NHK Television’s Weekly News Insights.
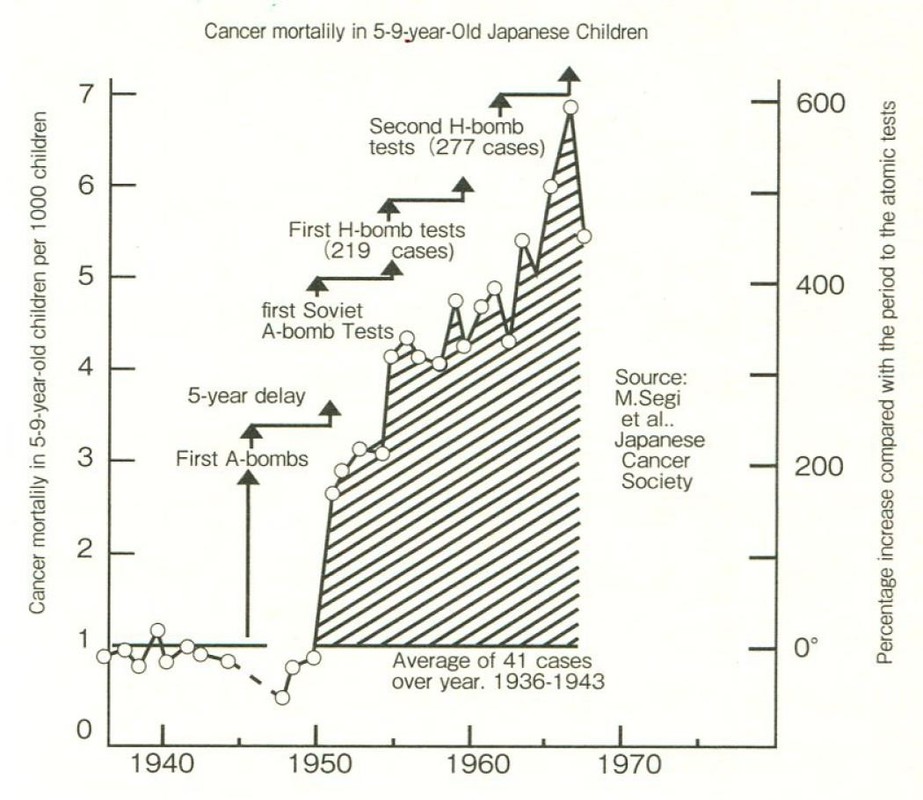
|
The NHK flipchart that disappeared was based on this graph. 2 |
I had asked them to make a flipboard for me which showed data on how the rate of child cancer deaths in Japan had jumped five years after the atomic bombings of 1945 to three times their original rate (see graph). It was data which clearly demonstrated that these children were the world’s first casualties of internal exposure. The night before the show, I was handed a script and sat in a meeting discussing the show until past 10 PM. However, the next morning, when I headed to NHK, the director told me that due to time constraints, we could not follow the script we had discussed the previous night. On entering the studio, the flipboard which I had expected to be at my feet was nowhere to be seen. When I asked a nearby staff member to please bring it for me, quickly, the reply was that they could not do that. With 30 seconds to go before showtime, I had no choice but to appear on the show bereft of my data.
The following day, when I requested a written explanation of these events, NHK did not oblige me. Faced against my will with such a situation, I feel strongly that I am responsible for not being able to properly deal with it.
The Society for Connecting Lives
My deceased wife, Okimoto Yaemi, established a society called “Connecting Lives – The Society to Connect Okinawa with Disaster Sites” together with Itō Michiko, an evacuee from Fukushima, and others. They demanded that the Tokyo Electric Power Company explain compensation claims to the victims of the disaster, and even made them come to Okinawa to explain this in person to the evacuees here. It was the first time TEPCO had travelled outside of Fukushima Prefecture to hold an information session. In Okinawa, a group of plaintiffs for a lawsuit to “return our livelihoods, return our region” also came together. 3
In the midst of all her work, Okimoto always came to send me off and to pick me up from Naha Airport. Now that she is gone, I have taken up her role as the representative for the “Connecting Lives” society.
After the accident, the melted-down reactor core was too radioactive to be properly disposed of. It is clear as day from this fact alone that nuclear power generation should not be permitted. In these 5 years, there has been a regime brimming with pollution: it is manifest in things like the lack of intelligence and care on the part of the Japanese government, the utilitarianism that places profits and power above human rights, and the political concealment of the worst environmental radiation disaster in history.
******
It is now 5 years since the Fukushima Daiichi accident, and we are in an abnormal state of affairs in which TEPCO and the national government are forcing people to silently accept their victimization.
Under the Atomic Energy Basic Law, the maximum annual exposure limit for the public is set at 1 millisievert. But people are being forced to accept a revised threshold that is 20 times larger, that of 20 millisieverts per year.
In Fukushima Prefecture, the cessation of compensation payments and the lifting of the evacuation order in highly contaminated regions has forced people to return, at the same time that housing support for the evacuees is also being ended. Of course, there are no measures at all in place to deal with radioactivity outside Fukushima Prefecture.
The Chernobyl NPP accident of 1986 led Ukraine (also Belarus and Russia) to establish laws that protected human rights, which stands in great contrast with the human rights situation surrounding the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident.4
Claiming Radiation Effects as Psychological
The media reports on the occasion of 3.11’s 5th anniversary contain references to the “fūhyō higai” (damage caused by rumors of radiation) that they claim is hampering the reconstruction process. Why do they not call this as it is, “radioactivity damage”? “Fūhyō higai”is a term that they use in order to replace radiation effects as psychological problems.
Under appointment of the IAEA, Shigematsu Itsuzō (now deceased), the former chairman of RERF(formerly ABCC), carried out a health survey of Chernobyl residents. He remarked in a report he made in 1990 that “there are virtually no diseases that are caused by radiation, but attention must be paid to the psychological stress that is caused by wondering whether or not one has been exposed to radiation”. The theory that “psychological stress causes illness” is a method used to conceal the radiation victimization of the nuclear age.
In Chernobyl, uncontaminated food was distributed to residents of contaminated areas. Respite trips for children are also ensured by the state. And yet, in Fukushima, there is a huge push to “support by consumption” (tabete ouen) and the administration has implemented a policy of “locally-grown and locally-consumed” in providing children’s school lunches. Japan is not attempting to avoid internal exposure as Chernobyl-affected states did; it is doing the exact opposite.
What is at the bottom of this response? Whether it is protecting residents from radiation exposure, or decommissioning of the melted reactor core, or indeed dealing with the contamination of underground water, there are numerous things that need to be addressed even by diverting the budgets of the forthcoming Tokyo Olympics. However, the Japanese government is trying to overcome all these issues with cheaper costs at the expense of people’s suffering. Underlying this is their utilitarianism – an ideology which prioritizes economics over human rights and human lives – as well as their philosophy of abandoning the people.
Following what the government is saying, one is left speechless. “If it’s under 100 becquerels, then sell it [produce]”; “If you don’t sell it you won’t be able to support yourself”; “If you talk about radioactivity you won’t be able to sell [your produce]”; “Don’t talk about radioactivity”. Media reports are controlled by the government, and people can only remain silent.
Providing safe food is the mission of agriculture. Surely there is no more cruel infraction of human rights than to force producers, against their will, to make food that might adversely affect human health by radioactive contamination. There is no solution to this injustice other than to get rid of this system that has been imposed by fiat. Although farmers’ labors have lowered the amount of radioactive contamination in their produce, tragedies will continue as long as they keep the allowable radioactivity in food up to 100 becquerels/kilogram.
Such standard stems from the thinking that economic profits comes before health. Radioactivity even in small amounts can cause harm. International Commission on Radiological Protection has it that carcinogenesis starts with DNA mutation of a single cell. Human susceptibility to radioactivity depends on individuals, and more vulnerable ones, particularly fetuses are affected first. The natural miscarriage rate of the four prefectures including Fukushima since 311 has risen by 13%.5
Consumption of one becquerel of C-137 (with biological half-life of approximately 80 days) every day will result in an internal accumulation of 140 becquerels within about 2 years. If we have to inevitably set any standard for allowable radioactivity in food, we should use the guidelines set forth in the recommendation by German Society for Radiation Protection, which is “no food with a concentration of more than 4 becquerel of the leading radionuclide Cesium-137 per kilogram shall be given to infants, children and adolescents. Grown-ups are recommended to eat no food over 8 becquerel per kilogram of the leading nuclide Cesium-137.”6
Deceitful Dosimetry
The Japanese government’s philosophy of abandoning its people starts with its refusal to trust them, in other words it views them as unintelligent citizens. Fearing that a panic would result, it did not announce SPEEDI data, nor did it distribute solid iodine tablets. It prioritized “emotional stability” over protecting residents from radiation danger. Moreover, it implemented thorough control of information.
It is not simply that residents are seen as ignorant. The government has even actively betrayed their trust. A classic example of such actions by the state is the presentation of data on the radioactive contamination levels in the environment. The government set up monitoring posts (MP) in Fukushima Prefecture and neighboring prefectures and made the readings from them into official data. Along with Yoshida Kunihiro and others from the “Safety and Reassurance Project”, in the autumn of 2011, I checked the dose measurements of the MP. We found clear evidence that the publicly available data of the MP only showed 54% of the actual level of contamination in our readings.
|
Comparison of Radiation Dose Readings from the Monitoring Posts and Actual Doses X-axis: amount of radiation (microsieverts/hour Y-axis: actual doses for residents and measurements at monitoring posts Black dot-dash line: Actual absorbed dose received by residents Dotted red line: Measurements at monitoring posts without decontamination Red line: Measurements at monitoring posts with decontamination [When laid alongside a graph of the actual recorded radiation doses taken by the authors at the monitoring posts (black line; the absorbed dose to residents), the same displayed readings taken from the same monitoring posts were 58% of that value in the case of non-decontaminated areas and 51% for decontaminated areas.] [2011 autumn, taken with a certified scintillator counter, model HITACHI-ALOKA YCS172B] |
On top of that, there was also a deliberate downplaying in government processing of the numerical data. The level of soil contamination is directly related to the amount of radiation in the air, and an objective measurement of this thus should be obtained from the air dose. However, on the assumption that there is a uniform exposure dose to the whole body, this reading was converted to 60% of its full amount based on the projected dose, an amount called the “effective dose”, a number that divides the exposure dose among the body’s various organs. Furthermore, they made a hypothetical estimate of the time people spent inside and outside their homes, and created a “substantive dose” reading that was another 60% lower. In the background to these machinations lies the will of the international nuclear energy industry.
The health survey being conducted by the Fukushima Prefecture Health Survey Evaluation Committee continues to progress, and the sad news is that it has already located 163 cases of cancer. From a scientific point of view, it is clear that these cases are undeniably caused by radioactivity. I also found, from the ratio of male to female patients, that about 75% of cancers in each sex were induced by radiation. Despite this, the Evaluation Committee continues to assert that there is no proof that these cancers are linked to the NPP accident.
Just as the committee insists that the numerous stark cases of thyroid cancer are not linked to radioactivity, so they will attempt to bury all other adverse health impacts in the sand.
******
Environmental pollution by radiation in Japan is ongoing, and, following the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident, it is the worst it has ever been. This is true whether we look at the amount of radioactivity being released via the long-term meltdown of the reactor core, which is spewing uncontrollably, while the government and mass media collaborate in the cover-up. From the standpoints of society, economics and preventative medicine, a terrible state of affairs will result if we do not provide public protection to the people affected by the accidents and clarify the nature and extent of environmental damage.
“Cheaper” Countermeasures
The Japanese government has deemed the amount of radioactivity released from the Fukushima accident as one sixth of that which was released from Chernobyl. However, the subsequent revelations suggest that Fukushima’s radioactivity is actually anywhere from 2 to 4 times as high as Chernobyl’s.7 Compared to the explosion of just one reactor at Chernobyl, which had a 1,000,000 kilowatt capacity, the explosion at Fukushima Daiichi involved 4 reactors with a combined output of 2,810,000 kilowatts.
The post-accident maintenance of nuclear reactors between Fukushima and Chernobyl also differs. Seven months after Chernobyl, a steel and cement sarcophagus was built to cover the reactor, thus stopping the further release of radioactive materials. Japan, even after 5 years, continues to let radioactive substances spew out into the air and water, thus worsening the world’s environment.
Without using the necessary basic procedures, they are simply trying to implement “cheaper” countermeasures. The fact that the stricken reactor cannot be managed alone can demonstrate that nuclear power lacks practicality and there is no choice but to abolish it.
As mentioned before, Japan is not honestly disclosing the degree of contamination and is using various measures to underestimate it. They have not published dose readings for radioactive nuclides such as uranium, plutonium, and strontium-90. The monitoring posts, which are supposed to provide public data of radioactivity, give readings that are only around half of the actual doses.
Pediatric thyroid cancer cases in Fukushima have risen to 163. It has been proven scientifically that these are due to radiation. (Tsuda Toshihide et al. have demonstrated this via statistics8; Takamatsu Isamu has examined the relationship between exposure dose and cancer onset rate9; Matsuzaki Michiyuki10 and Yagasaki Katsuma11have studied the relationship of radiation with the sex-differentiated ratio of cancer).
In response to this research, the Fukushima Prefectural Health Evaluation Committee has continued to insist that there is no clear link between cancer and the NPP accident. They are trying to bury all the injuries to health by this denial of a link between radioactivity and the many recorded cases of thyroid cancer. By expunging the record of health damages caused by radiation, they hope to heighten the false impression that NPPs are “safe”. In Japan, excessive utilitarianism goes unmentioned; companies’ profits and the state’s convenience take priority over human life.
The Systemization of Dispersal
The countries surrounding Chernobyl created a “Chernobyl Law” to protect their residents 5 years after the accident. Under this law, the government designated areas that received more than 0.5 millisieverts of radiation each year as “dangerous”, and areas that received between 1 and 5 millisieverts of radiation each year as “areas with relocation rights”, while areas receiving more than 5 millisieverts each year could not be used as residential or agricultural sites. Health checkups and respite trips for children have been covered in a massive budgetary investment by the state in order to protect its residents.
What about Japan? The legal exposure limit for the public is 1 millisievert per year. As previously mentioned, the government has raised the upper threshold to 20 millisieverts per year in their drive to push Fukushima residents to return. The Chernobyl law forbids residence and agriculture in areas where more than 5 millisieverts (per year) of irradiation is expected; in Japan, approximately 1,000,000 people live in such areas.
Under the Basic Law on Atomic Energy, which governs nuclear reactors and related phenomena, the standard for radioactive waste management (the level considered for safe recycling use) is 100 becquerels per kilogram. Notwithstanding this rule, the special law for measures to handle contamination by radioactive substances permits up to 8000 becquerels per kilogram. Contamination dispersal is thus becoming systematized.
A law to support child victims was established, but no maps of radioactive contamination were made, and the areas specified to receive assistance under this law’s “Basic Policy” are limited to Fukushima Prefecture. With this law they have thus made all areas outside Fukushima Prefecture ineligible to receive radioactivity countermeasures.
When looking at the measurements taken by the Nuclear Regulation Authority of the contamination levels in all prefectures, we see that contamination exists everywhere in the country, Okinawa being no exception.
In particular, eastern Japan shows high levels of contamination. Ten prefectures showed contamination of more than 1,000 becquerels of Iodine-131 per square meter of land–Tochigi, Ibaraki, Tokyo, Yamagata, Saitama, Chiba, Gunma, Kanagawa, Nagano, and Shizuoka (Readings for Fukushima and Miyagi were not available for a period of time because the measurement equipment were destroyed by the earthquake and tsunami, but other sources confirm high I-131 dispersion in Fukushima). Eleven prefectures showed more than 1,000 becquerels of Cesium-137, and Cesium-134–Fukushima, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Tokyo, Yamagata, Saitama, Chiba, Gunma, Kanagawa, Iwate, and Nagano (based on Yagasaki’s analysis of the NRA monitoring data of March 2011 to January 2014).12
These readings are taken from a fixed point, which means that if a radioactive plume does not pass over these points, it will not be measured, and is liable to produce an under-estimation gap by 1 to 2 digits.
Although the Ministry of Education has implemented airborne monitoring, cities with a density of buildings higher than 3 stories present obstacles to this technology, making it unable to record their levels of contamination. Severe contamination is concealed in the Tokyo metropolitan area and other places in the region.
Legal Protection of Citizens
The above facts demonstrate an intentional ignoring of the serious level of radiation pollution. Japanese citizens should recognize radioactivity pollution as a de facto state of affairs.
In order to protect Japanese citizens from radioactivity pollution, the government and administration should take responsibility for protecting victims via a swift application of the regulations exactly as they are laid out under the Basic Law on Atomic Energy. Here we raise some suggestions for administrative policies to enact not only towards evacuees, but all residents.
- The state should recognize and guarantee citizens’ right to evacuate and relocate. It should also bear responsibility in enacting measures to protect vulnerable victims, especially children.
- Health damages that emerge from NPP accidents should be studied on a nation-wide scale, and a study of the conditions of evacuees should be quickly implemented.
- Those most vulnerable to radiation should be protected by measures based on a sincere commitment to preventive medicine.
- With regard to the numerous early-onset cases of child thyroid cancer that have far exceed such early cases caused by Chernobyl, medical care and compensation should be provided; children and all residents should be protected. Thyroid screening should also be carried out for the entire country.
- Measures to prevent the entrance and exit of radioactive substances in all regions should be enacted.
- TEPCO’s social responsibility as a victimizer corporation in radioactivity pollution should be clarified.
This is a translation of a modified version of Yagasaki’s three-part article series “Kakusareru naibu hibaku – Fukushima genpatsu jiko no shinso” that appeared in Ryukyu Shimpo on March 16, 17, and 18, 2016.
Notes
Internal radiation refers to ingestion of radiation through inhaling radioactive dust or consumption of radioactive food and water.
Graph comes from Ralph Graeub: The Petkau Effect, Four Walls Eight Windows, New York (1994), p.70. Original data is from: M. Segi and M. Kurihara: Cancer Mortality for Selected Sites in 24 Countries, Japan Cancer Society, Tohoku University, Japan, Nov., 1972.
As of February 1 of 2016, the number of evacuees to Okinawa was 707. (This number does not include the evacuees from outside of Fukushima Prefecture. See here.)
Japanese translation of the “Chernobyl Laws” is available as part of the full report by the “House of Representatives Delegation for Investigation of Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Accident (衆議院チェルノブイリ原子力発電所事故等調査議員団報告),” December, 2011.
Scherb, Fukumoto, Voigt, Kusmierz, フクシマの影響 日本における死産と乳児死亡, which is a translation of an extended version of the article “Folgen von Fukushima, Totgeburten und Säuglingssterblichkeit in Japan” that appeared in the February 6, 2014 edition of Strahlentelex, a German journal specializing on radiological protection. More information about ongoing health effects of Fukushima.
“Recommendations to Minimize Radiation Risk by Internal Exposure in Japan,” German Society for Radiation Protection, March 20, 2011.
The Chernobyl accident only involved aerial radioactive dispersion, but Fukushima in addition includes water and ocean contamination. A calculation with these into consideration renders such ratios. Watanabe Etsushi, Endo Junko, Yamada Kosaku, Hoshasen hibaku no soten, Ryokufu Shuppan, 2016, p. 170 –
Tsuda et al. Epidemiology 2015 Oct. 5:Tsuda T, Tokinobu A, Yamamoto E, et al. Thyroid Cancer Detection by Ultrasound Among Residents Ages 18 Years and Younger in Fukushima, Japan: 2011 to 2014. Epidemiology 2015 Oct 5.
Matsuzaki Michiyuki, “Report on the Seikatsu Kurabu Thyroid Examination,” July 19, 2015 at Hibiya Convention Hall, Tokyo (Slides 73-101)
Nuclear Regulation Authority, “Teiji kōkabutsu no monitoring,” Monitoring information of environmental radioactivity level.