Abstract: This article assesses the US debacle in Afghanistan in light of the Vietnam War and US forever wars.
U.S. Army soldiers from the 10th Mountain Division return home from a nine-month deployment to Afghanistan at Fort Drum, New York, on Dec. 10, 2020.
The Warning Signs
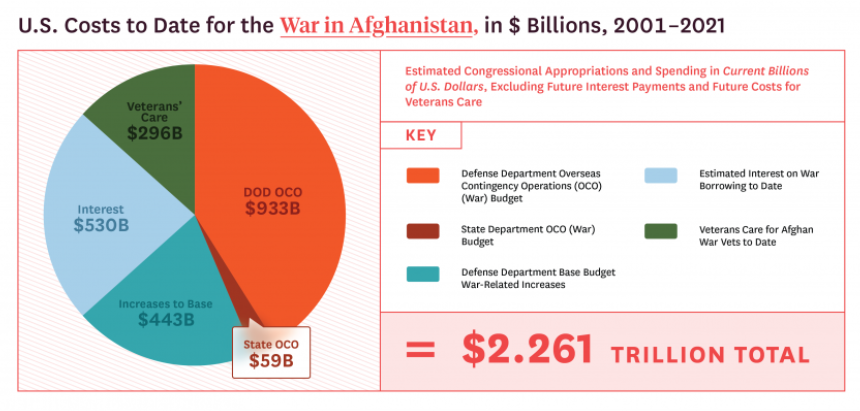
Over a nearly twenty-year period, the US war in Afghanistan is estimated to have cost about $2.2 trillion and resulted in over 240,000 deaths, military and civilian, on all sides. (See the relevant charts below from the Costs of War Project at the Watson Institute, Brown University.) Now, as we watch the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan, we may pause—as we did on Vietnam in 1975—to wonder how things could have gone so badly after such an extraordinary investment of blood and treasure. But in truth there’s no reason to wonder: Precisely because of the defeat in Vietnam, the underlying reasons for the Afghanistan debacle should have been anticipated, in fact were identified years ago, and should have dictated nonintervention or early withdrawal. We were warned, but presidents from George W. Bush to Donald Trump chose to continue the intervention just as presidents during the Vietnam war chose, despite numerous signs of failure in conception and not merely in execution.
I’m just one observer, and far from the most expert, but I did note the warning signs some time ago. In October 2015 I wrote (Post #96): “We are now witness in Afghanistan to the same scenario US presidents confronted in Vietnam: public lies, private doubts. While the US military is reassuring the public that Afghan forces are up to the task of defeating the Taliban, the situation on the ground is anything but reassuring. Afghan government forces are in retreat, the ISIS organization in Afghanistan (many are former Taliban) is expanding operations, al Qaeda and Taliban forces remain strong, and US drone strikes continue to hit civilian targets. The ‘endless war’ [Obama] sought to avoid is a reality—something he should have foreseen, and for all we know did foresee, years ago.” But rather than withdraw from Afghanistan in the face of looming defeat, Obama did what Lyndon Johnson did in Vietnam: He increased US forces.
Pathologies of Decision Making
When the Washington Post published what it calls the “Afghanistan Papers” at the end of 2019, based on interviews that included many US civilian and military officials, we learned that the roots of failure had been widely known. For example, John F. Sopko, who in 2014 served as special inspector general for Afghanistan reconstruction, told the House Foreign Affairs Committee that U.S. officials have routinely lied to the public throughout the war. They exaggerated Taliban casualties, understated Afghan military success, and massaged data to show gains in Afghans’ education and health care— even though they “knew the data was bad.” “There’s an odor of mendacity throughout the Afghanistan issue . . . mendacity and hubris,” Sopko said in testimony. . . “The problem is there is a disincentive, really, to tell the truth. We have created an incentive to almost require people to lie” (Washington Post, January 14, 2020). And what US officials didn’t lie about, they classified, said Sopko: “It turns out that everything that is bad news has been classified for the last few years,” referring to the Trump administration.
Official lying and data manipulation are just two of the elements of decision making failure that are strikingly similar to what I found in the Pentagon Papers. Among them:
- Unwarranted optimism
- Confusion of activity (money and projects) with impact
- Lack of clarity about what winning means
- Persistence in believing in nation building
- Prioritizing military over economic and social needs
- Failing to reflect on basic assumptions
- Americanization of “their” war.
Options?
Joe Biden will likely pay the political price for the failure of his predecessors to confront those disorders. As in critiques of Vietnam decision making, Biden will be taken to task for not seeking total victory, for abandoning the Afghanis, for not staying in Afghanistan at lower cost, and for failing to anticipate the speed of the Taliban nationwide victory.. Total victory is and always has been a pipe dream: If a half million troops couldn’t “win” in Vietnam, it’s ridiculous to think that several hundred thousand troops could win in Afghanistan. The abandonment critique is also easily refuted: Trump’s call to get out under the cover of a spurious agreement with the Taliban could have led to US withdrawal several months earlier than Biden’s timetable called for.
The low-cost option, which Steve Coll has recently proposed, would amount to “a sustained, smaller deployment—not free, but nothing like the expenditures of the past—linked to a search for some more sustainable political outcome . . . ” (Interview with Isaac Chotiner, “How America Failed in Afghanistan,” The New Yorker, August 15, 2021.) This option, too, is not persuasive: It repeats the Vietnam error of false choices. In this bureaucratic game, an Option B is created for the president that is designed to be more palatable than either Option A, escalation, or Option C, withdrawal. But Option B rests on the delusion that both the costs (to America) in lives and dollars, and the political optics (for the president) of fewer body bags, will improve matters for an invading force just because the US profile will be lower. The “sustainable” option does nothing to promote a peaceful outcome or help the long-suffering Afghan people, but it does promise continuation of the endless war. In a word, it’s an immoral choice and an ineffective one.
The real options in Afghanistan were most fundamentally constrained by American exceptionalism and hubris at the highest levels, just as they were in Vietnam. As Robert McNamara observed, years too late, in his memoir, In Retrospect: The Tragedy and Lessons of Vietnam:
We did not recognize that neither our people nor our leaders are omniscient. Where our own security is not directly at stake, our judgment of what is in another people’s or country’s best interest should be put to the test of open discussion in international forums. We do not have the God-given right to shape every nation in our own image or as we choose.
Sadly, the Afghan debacle underlines the fact that our leaders can’t seem to learn that lesson.
Watson Institute, Brown University, Costs of War Project: